Been working on a nice project lately. My current client has chosen to run Grafana Cloud and the instance was running in West US, which was leading to slower performance. I took up the project of provisioning a new instance in West Europe. Although I would have preferred to host Grafana ourselves or use Azure Managed Grafana, this is what the client has chosen so I that is what I’ll have to work with.
Also taking the opportunity to refactor the IaC and review our authrozation methods. We were using LBAC but I would rather use RBAC.
A few goals for the configuration:
- Authentication to the Grafana Cloud instance must happen through Entra ID
- User management is based on Entra ID groups
- Teams within Grafana are automatically syched with Entra ID groups
- In other words, if a new user is added to an Entra ID group, it must automatically be added to the team in Grafana
To provision the instance I used the following terraform code. First we need the providers.tf:
terraform {
required_version = "~> 1.4"
required_providers {
grafana = {
source = "grafana/grafana"
version = ">= 1.40.1"
}
}
}
provider "grafana" {
alias = "grafana_cloud"
cloud_api_key = var.grafana_api_key
}
# Provider for managing the content of the Grafana Cloud instance
provider "grafana" {
alias = "content"
url = grafana_cloud_stack.vanoord_stack.url
auth = grafana_cloud_stack_service_account_token.cloud_sa.key
}
Here I’m declaring a provider for provisioning the cloud instance itself, “grafana_cloud”, and a second one to manage the content.
Next we provision the instance and service accounts, in cloud-instance.tf :
resource "grafana_cloud_stack" "vanoord_stack" {
provider = grafana.grafana_cloud
name = "vanoord"
slug = "vanoord"
region_slug = "prod-eu-west-3" # Example "us","eu" etc
}
resource "grafana_cloud_stack_service_account" "cloud_sa" {
provider = grafana.grafana_cloud
stack_slug = grafana_cloud_stack.vanoord_stack.slug
name = "terraform-serviceaccount"
role = "Admin"
is_disabled = false
}
resource "grafana_cloud_stack_service_account_token" "cloud_sa" {
provider = grafana.grafana_cloud
stack_slug = grafana_cloud_stack.vanoord_stack.slug
name = "terraform-serviceaccount-key"
service_account_id = grafana_cloud_stack_service_account.cloud_sa.id
}
resource "grafana_folder" "mischa" {
provider = grafana.content
title = "Mischa Test Folder"
}
Next I configured the instance to enable authentication with Entra ID. The process was quite straight forward and I used this documentation:
However, make sure to add this configuration under “Token Configuration” in the App Registration:
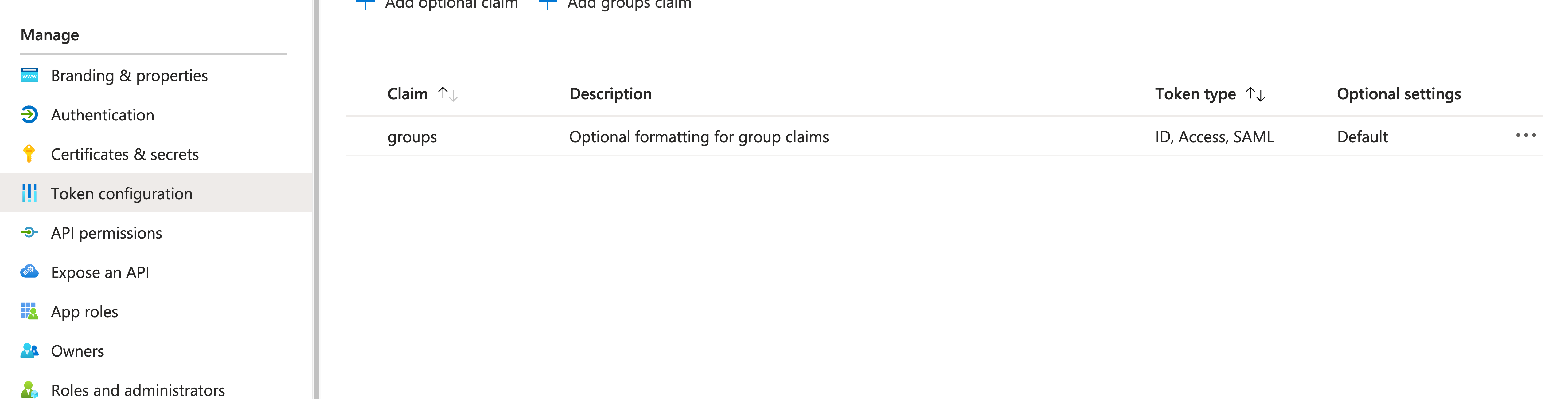
And add the following Graph API permissions:

When adding a new team, the group ID’s of the Entra ID groups must also be added to the Grafana Cloud instance in Grafana Cloud under Security -> Advanced Auth -> Azure AD -> Configure -> Allowed Groups.
Finally, to automatically synch the memebers of the Entra ID groups to teams in the Grafana Cloud instance, I wrote the following code:
locals {
teams = {
"team1" = { "AADGroupObjectIds" = ["id1"] },
"team2" = { "AADGroupObjectIds" = ["id2"] },
}
}
resource "grafana_team" "teams" {
provider = grafana.content
for_each = local.teams
name = each.key
ignore_externally_synced_members = false
team_sync {
groups = each.value.AADGroupObjectIds
}
}
With this setup the members of the Entra ID groups are automatically synched to the teams in Grafana Cloud.
In the next article I’ll add data sources and authorize teams to data sources and other resources within Grafana.
Links:
202311171711
[[Azure]]
[[grafana]]